Common Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry
Common Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry can be organized by functional groups – specific groupings of atoms that have characteristic structures and chemical behaviors. Recognizing functional groups in an organic molecule is crucial because they largely determine how that molecule will react. Each functional group can be thought of as a distinct "unit" within a molecule, and molecules with the same functional group often undergo similar types of reactions.
Below is a summary of the most common functional groups in organic chemistry, categorized by the atoms and bonds involved:
Hydrocarbons
These functional groups consist only of carbon and hydrogen in various bonding arrangements:
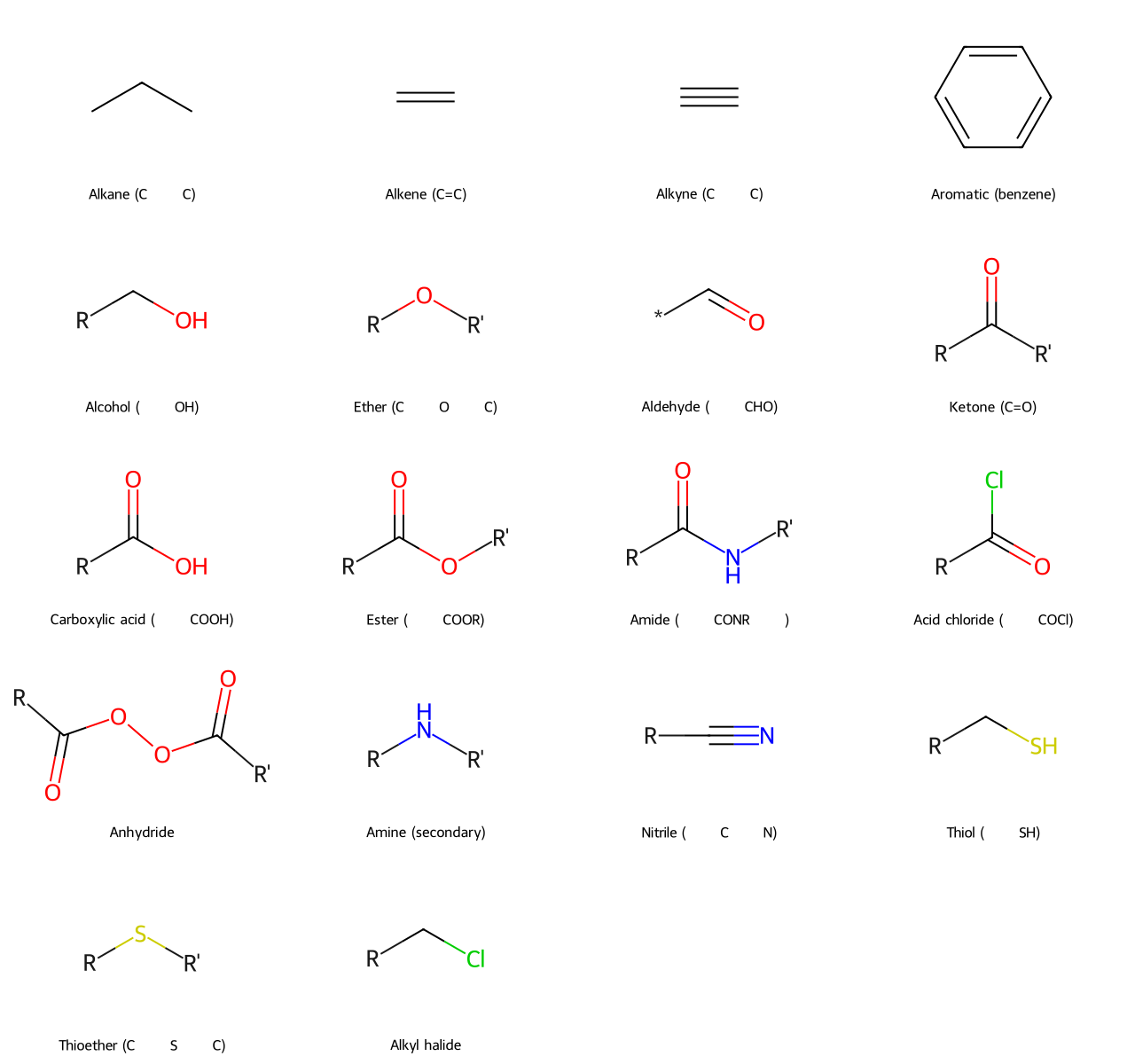
- Alkane (C–C single bonds): Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons containing only single bonds between carbon atoms. They have the general formula CₙH₂ₙ₊₂ (for acyclic alkanes). Example: Ethane (C₂H₆) is a simple alkane with a C–C single bond.
- Alkene (C=C double bond): Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon–carbon double bond. General formula for one double bond is CₙH₂ₙ (assuming a single double bond and no rings). Example: Ethene (C₂H₄, also called ethylene) has a C=C double bond.
- Alkyne (C≡C triple bond): Alkynes contain at least one carbon–carbon triple bond. General formula for one triple bond is CₙH₂ₙ₋₂. Example: Ethyne (C₂H₂, common name acetylene) has a C≡C triple bond.
- Aromatic (benzene ring and derivatives): Aromatic compounds typically contain a benzene ring or similar ring systems with delocalized π electrons (following Hückel’s rule). Example: Benzene (C₆H₆) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon, consisting of a six-membered ring with alternating double bonds (delocalized into a stable aromatic sextet).
Halogen-Containing
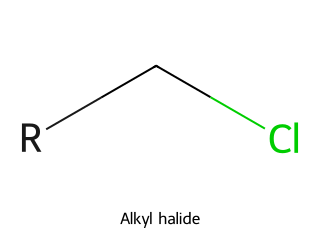
- Alkyl Halide (Haloalkane): An alkane in which one or more hydrogens has been replaced by a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I). They are named as fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, or iodo- alkanes. Example: Chloromethane (CH₃Cl) is a simple alkyl halide.
Oxygen-Containing Functional Groups
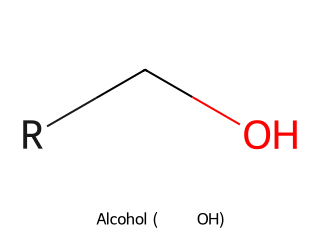
- Alcohol (–OH group): Alcohols contain a hydroxyl group (–OH) bonded to a tetrahedral (sp³) carbon. Example: Ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) has an –OH group on an ethyl chain.
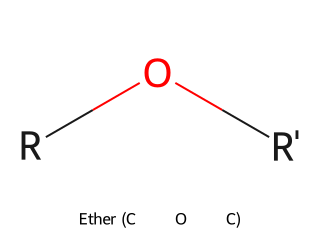
- Ether (C–O–C linkage): Ethers have an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. General structure R–O–R'. Example: Diethyl ether (CH₃CH₂–O–CH₂CH₃) is a common ether.
- Carbonyl Compounds: These contain a carbon–oxygen double bond (C=O), known as a carbonyl group. The nature of the other atoms attached to the carbonyl defines the specific functional group:
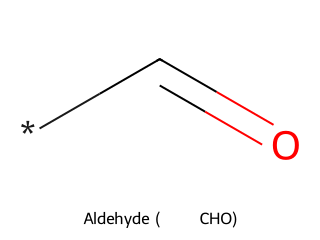
- Aldehyde: Carbonyl with at least one hydrogen attached (general form R–CHO). Example: Acetaldehyde (CH₃CHO) has a carbonyl bonded to one H and one CH₃.
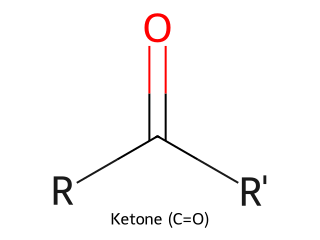
- Ketone: Carbonyl with two carbons attached (general form R–CO–R'). Example: Acetone (CH₃COCH₃) has a carbonyl bonded to two CH₃ groups.
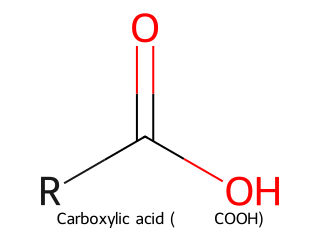
- Carboxylic Acid: Carbonyl with an –OH attached (–COOH group). General formula R–COOH. Example: Acetic acid (CH₃COOH) has a carboxyl group.
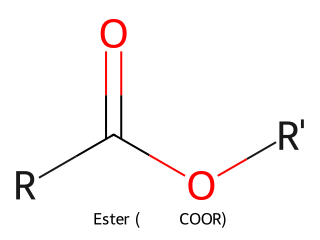
- Ester: Carbonyl with an –OR attached (–COOR'). Essentially a carboxylic acid where the –H is replaced by an alkyl group. Example: Ethyl acetate (CH₃COOCH₂CH₃) is an ester.
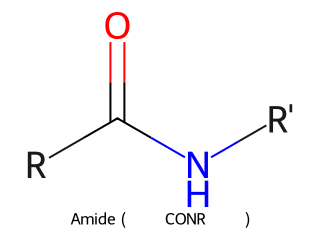
- Amide: Carbonyl with an –NR₂ attached (where R can be H or carbon substituents). General form R–CONR₂. Example: Acetamide (CH₃CONH₂) has a carbonyl attached to an –NH₂.
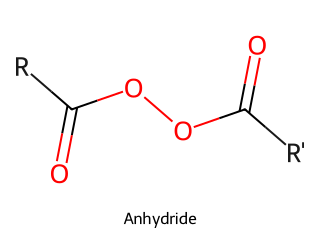
- Acid Anhydride: Two carbonyls bonded to an oxygen (R–CO–O–CO–R). Often formed from two carboxylic acids by dehydration. Example: Acetic anhydride ((CH₃CO)_2O).
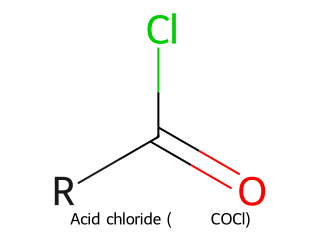
- Acid Halide (Acyl Halide): Carbonyl attached to a halogen (R–CO–X, where X = F, Cl, Br, I). Example: Acetyl chloride (CH₃COCl).
Nitrogen-Containing Functional Groups
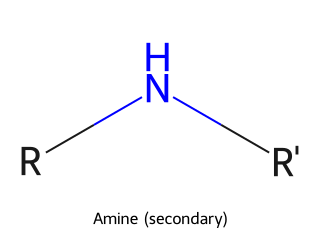
- Amine: Derivatives of ammonia (NH₃) where one or more hydrogens are replaced by carbon groups. They are classified as primary (RNH₂), secondary (R₂NH), or tertiary (R₃N) depending on how many carbon groups are attached to the nitrogen. Example: Methylamine (CH₃NH₂) is a primary amine.
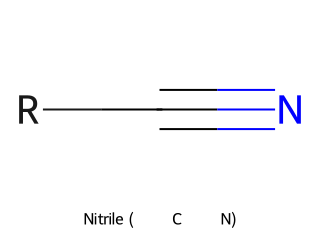
- Nitrile (Cyano group, –C≡N): Contains a carbon triple-bonded to a nitrogen. Example: Acetonitrile (CH₃CN) has a –C≡N group.
Sulfur-Containing (Less Common in Basic Organic Chemistry)
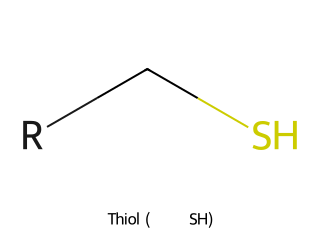
- Thiol (Mercaptan, –SH group): Analogous to alcohols but with sulfur in place of oxygen. Example: Ethanethiol (CH₃CH₂SH) has a thiol group.
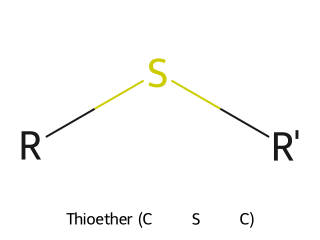
- Thioether (Sulfide, C–S–C): Analogous to ethers with sulfur replacing oxygen. Example: Dimethyl sulfide (CH₃–S–CH₃).
Each functional group imparts certain physical and chemical properties. For instance, alcohols and carboxylic acids can engage in hydrogen bonding (affecting boiling points and solubility), while alkenes and alkynes undergo addition reactions at their multiple bonds. Recognizing these groups in structures is the first step to predicting reactivity.
In more advanced study of organic chemistry, specific reactions and properties associated with each functional group are covered. This foundational identification of functional groups provides a vocabulary for classifying organic molecules and understanding their behavior.
Summary
Organic molecules are categorized by their functional groups, which are specific atoms or bonds responsible for characteristic chemical reactions. Key groups include hydrocarbons like alkanes (all single bonds), alkenes (double bonds), alkynes (triple bonds), and aromatics (delocalized rings); oxygen-containing groups such as alcohols, ethers, and a variety of carbonyl-containing functional groups (aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, etc.); nitrogen-containing groups like amines and nitriles; as well as others like halides and thiols. Recognizing functional groups in a molecule is essential for understanding its reactivity and properties, as molecules with the same functional group tend to react in similar ways. This knowledge lays the groundwork for studying organic reactions and synthesis.