Chapter 1 Practice Problems
Chapter 1 Practice Problems
Use these problems to reinforce Chapter 1 basics. Try each prompt before expanding the answers.
Lewis Structures & Formal Charge
- Draw the bicarbonate ion. Indicate formal charges on each atom.
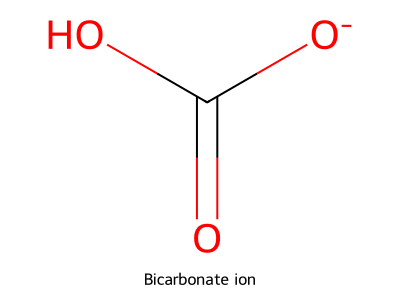
Answer
Major contributor: HO–C(=O)–O⁻ with the negative charge on one oxygen (resonance-shared between the two singly bonded oxygens). Carbon and the double-bonded oxygen are neutral; the deprotonated oxygen is –1; overall –1 charge.
Hybridization & Geometry
- For glycine (shown), assign the hybridization of the nitrogen and carbonyl carbon; describe their geometries.
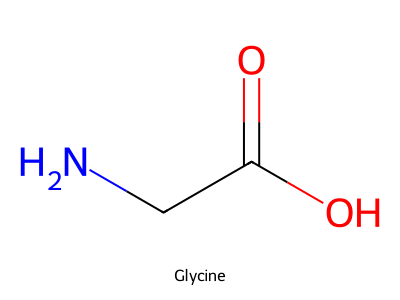
Answer
N is sp³, trigonal pyramidal (lone pair + three σ bonds). The carbonyl carbon is sp², trigonal planar (~120°).
Naming & Functional Groups
-
Provide the IUPAC name for the alcohol below.
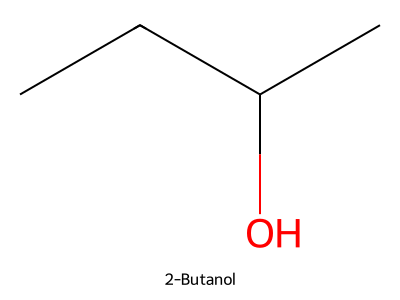
Answer
2-Butanol (butan-2-ol). -
Identify all functional groups in HOCH₂CH₂NHCOCH₃.
Answer
Primary alcohol (–CH₂OH) and a secondary amide (–NH–C(=O)–CH₃).
Acid–Base Strength
- Which is the stronger acid: acetic acid or ethanol? Give the key reason.
Answer
Acetic acid; its conjugate base (acetate) is resonance-stabilized, whereas ethoxide is not.
Isomerism & Stereochemistry
-
Classify the pair below (relationship).
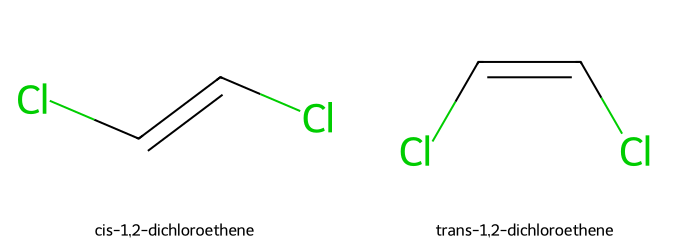
Answer
Diastereomers (geometric isomers: cis vs trans). -
Is the alcohol above (Problem 3) chiral? Describe the enantiomers briefly.
Answer
Yes. The OH-bearing carbon has four different groups; the two enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images with opposite R/S configuration at C-2.
Physical Properties
- Which boils higher: n-hexane or 2,2-dimethylbutane?
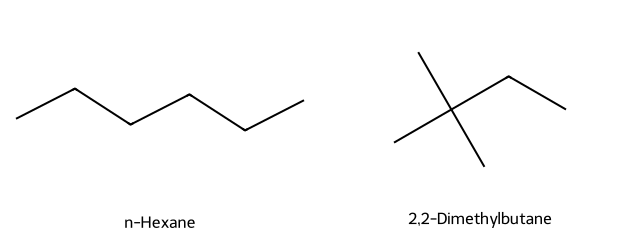
Answer
n-Hexane; its less-branched shape gives stronger dispersion forces than the compact 2,2-dimethylbutane.
Reactivity Basics
-
Propane undergoes radical chlorination. Which product predominates?
Answer
2-Chloropropane (secondary radical pathway is favored over primary). -
Write the balanced combustion for cyclopentane.
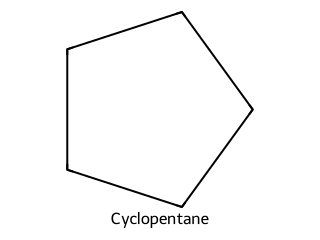
Answer
2 C₅H₁₀ + 15 O₂ → 10 CO₂ + 10 H₂O.