Reactions of alkanes, including combustion and halogenation
Reactions of Alkanes: Combustion and Radical Halogenation
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that are relatively inert, yet two reactions matter most in introductory organic chemistry: combustion and free-radical halogenation (Cl₂ or Br₂). Both can be summarized with simple equations, but halogenation requires understanding radical chain mechanisms and selectivity.
Combustion of Alkanes
Complete combustion converts an alkane to carbon dioxide and water:
CxHy + (x + y/4) O₂ ⟶ x CO₂ + (y/2) H₂O
Key points:
- Highly exothermic; requires a spark or sufficient heat to initiate.
- Adequate oxygen gives a clean burn (CO₂ + H₂O).
- Oxygen-poor conditions yield CO, soot, and partially oxidized byproducts (aldehydes, ketones).
- Longer/more reduced hydrocarbons release more energy per mole; combustion is a redox process (carbon oxidized, O₂ reduced).
Butane
O₂
CO₂

H₂O
Radical Halogenation (Cl₂ / Br₂)
Radical halogenation replaces a hydrogen with a halogen via a free-radical chain:
R-H + X₂ ⟶ R-X + H-X (X = Cl, Br)
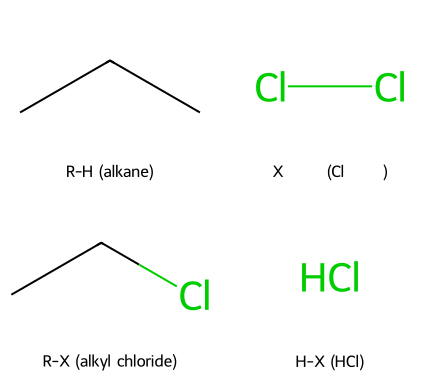
Chain mechanism
Initiation
X₂ ⟶[hν or Δ] 2 X·
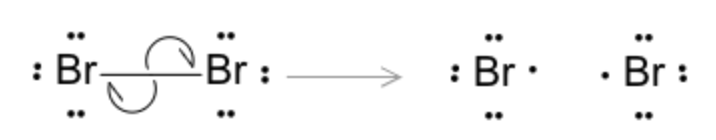
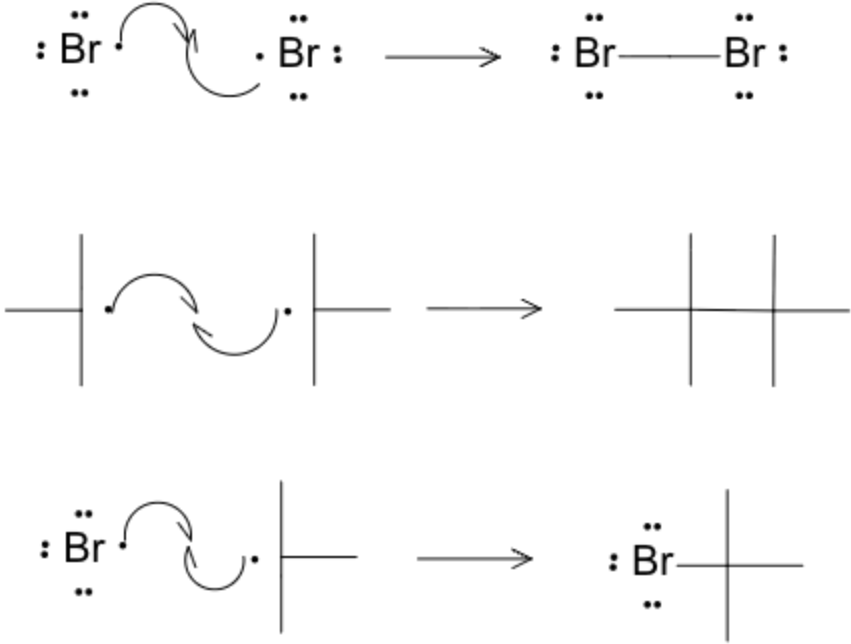
Propagation
R-H + X· ⟶ R· + H-X
R· + X₂ ⟶ R-X + X·

Termination
Radicals recombine, e.g.:
X· + X· ⟶ X₂, R· + X· ⟶ R-X, R· + R· ⟶ R-R
Reactivity and Selectivity
- Relative C–H reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary.
- Chlorination: fast, less selective (≈5 : 3.5 : 1 ratio for tertiary:secondary:primary), so mixtures of mono-, di-, polyhalogenated products form.
- Bromination: slower, more selective; strongly favors tertiary C–H and gives one major product when conditions are tight.
- Fluorination: too exothermic/violent for standard lab halogenation.
- Iodination: endothermic and generally not synthetically useful under these conditions.
Downstream Functionalization
- The alkyl halide product can undergo nucleophilic substitution (SN1/SN2) or elimination (E1/E2), opening paths to alcohols, ethers, alkenes, etc. Radical halogenation is thus a gateway to further diversification.
- Cracking/reforming (industrial) also converts long alkanes into shorter alkanes/alkenes using heat and catalysts.
Summary
- Combustion: balance C, H, O → CO₂ + H₂O; the stoichiometric recipe ensures a clean burn under excess oxygen.
- Free-radical halogenation: understand initiation/propagation/termination, remember tertiary > secondary > primary, and know that bromination is more selective than chlorination.
- Focus on substitution at sp³ C–H bonds; this is not an addition reaction.