Common Alkene Reactions: Electrophilic Additions
Common Alkene Reactions: Electrophilic Additions
Alkene π bonds are electron-rich and typically react with electrophiles. Most introductory reactions add two atoms/groups across C=C, with predictable regiochemistry and stereochemistry.
Key Addition Patterns
- Hydrogenation (H₂/Pt, Pd, Ni): syn addition of H/H → alkane.
- Halogenation (X₂): anti addition of X/X via halonium → vicinal dihalide.
- Hydrohalogenation (HX): Markovnikov addition of H/X; beware rearrangements.
- Hydration (H₂O/H⁺): Markovnikov H/OH → alcohol (rearrangements possible); other methods avoid rearrangements.
- Halohydrin (X₂/H₂O): anti addition; OH to more substituted carbon, X to less.
- Dihydroxylation (OsO₄ or cold KMnO₄): syn OH/OH → vicinal diol.
- Epoxidation (peracids like mCPBA): syn oxygen delivery → epoxide; acid opening gives anti diol.
Representative Examples
Hydrogenation (H₂/Pt, Pd, Ni): Catalytic hydrogenation reduces alkenes to alkanes by passing H₂ over a supported metal such as Pd/C, Pt/C (or PtO₂), Raney Ni, or Rh/C. Both H₂ and the alkene chemisorb on the metal surface: H₂ first dissociates to M–H, the alkene π-binds, and two successive surface hydride transfers deliver H atoms syn across the C=C bond (Horiuti–Polanyi sequence). When both alkene carbons become stereocenters, the products are racemic under achiral conditions. Mind competing reductions—Pd/Ni can hydrogenolyze benzyl protecting groups and reduce nitro/azide/carbonyl functions; aromatics typically require harsher Ni/high-pressure conditions. See the full guide on alkene hydrogenation for mechanism panels and catalyst tips.
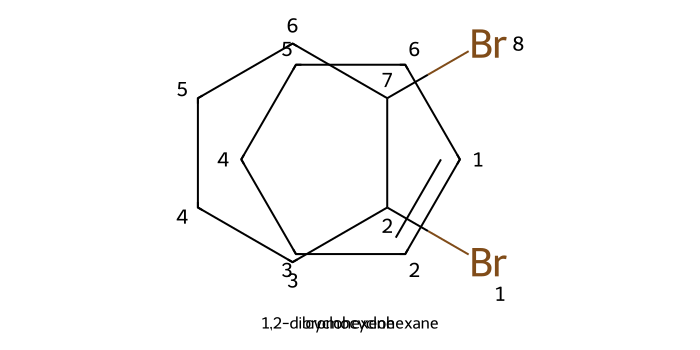
Halogenation (X₂): Adding bromine (Br2) to an alkene will form a dibromide, causing a bromine functional group to be added to each carbon on either side of the double bond.
The two bromines are added in an anti fashion, meaning that the stereochemistry of each bromine will be opposite of the other.
For more information on bromination reactions, check out our Reaction Library
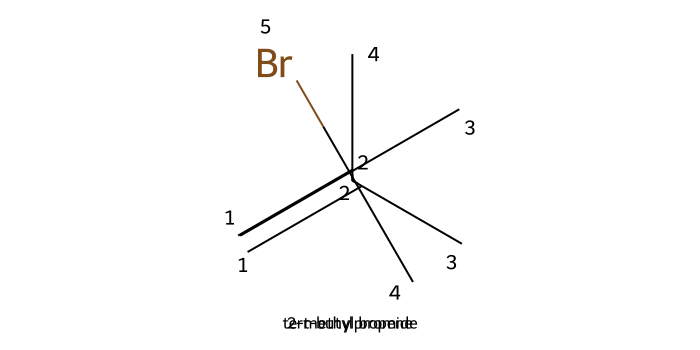
Hydrohalogenation (HX): Alkenes react with hydro halogens (HX) to form alkyl halides.
If there are carbon atoms adjacent to the reaction site that are more highly substituted than those on the alkene bond, a methyl or hydride shift can occur.
For more information on hydrohalogenation reactions, check out our Reaction Library
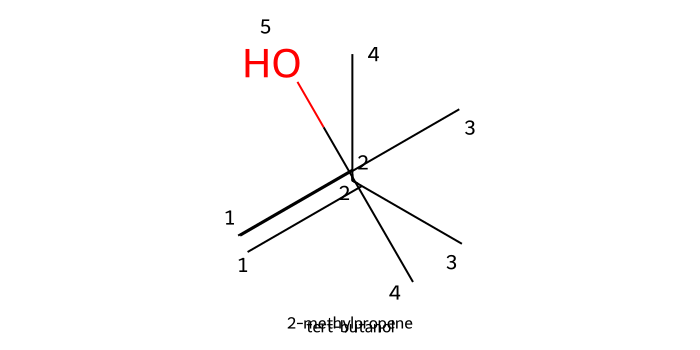
Hydration (H₂O/H⁺): Dilute H2SO4 or H3O+ adds water across an alkene to give the Markovnikov alcohol via a carbocation; hydride or methyl shifts are possible.
For the full mechanism and exam tips, see the Alkene -> Alcohol with aqueous acid guide.
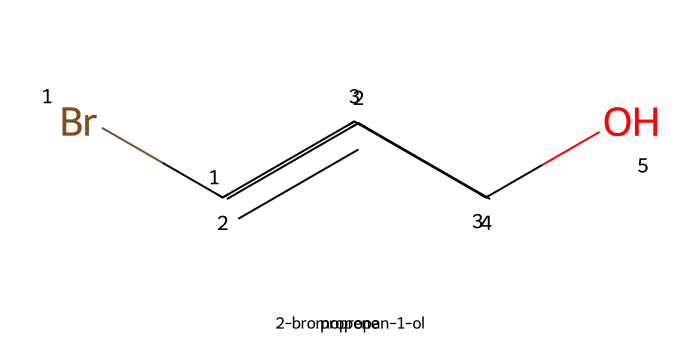
Halohydrin (X₂/H₂O): Adding bromine (Br2) or N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) to a solution containing water (H2O or H2S) and an alkene will result in the formation of a bromohydrin
The bromine is added first, followed by a backside attack from the water (or hydrogen sulfide) molecule.
This backside attack results in an anti addition for these two functional groups; the Br group will have a different stereochemistry than the OH group.
For more information on bromohydrin formation, check out our Reaction Library
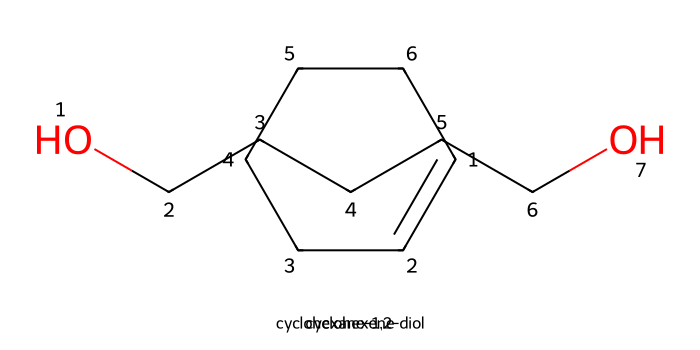
Dihydroxylation (OsO₄ or cold KMnO₄): Osmium tetroxide (OsO4), in combination with H2O and NaHSO3, react with alkenes to form vicinal diols (1,2-diol)
The shape of OsO4 makes it so that the most favorable bonding for the intermediate has syn stereochemistry branching from the alkene to the OsO4 moiety.
If after binding to the OsO4 molecule the alkene does not generate new stereocenters, there will be no stereochemistry configuration
For more information on other diol forming reactions, check out our Reaction Library
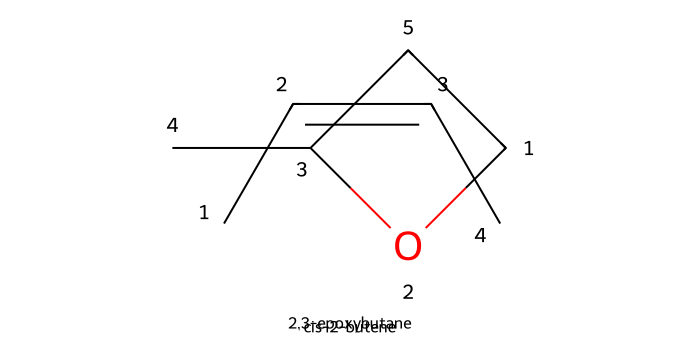
Epoxidation (peracids like mCPBA): mCPBA (and other peracids) epoxidize alkenes in a single concerted step, transferring oxygen across the π bond while preserving the alkene’s original geometry.
Electron-rich alkenes react fastest, and the m‑chlorobenzoic acid by-product is removed with a mild NaHCO₃ wash after the reaction.
For more information on alkene epoxidation with mCPBA, check out our Reaction Library
Summary
- Alkenes typically undergo electrophilic addition: X/X, X/OH, H/X, H/OH, H/H, OH/OH, or epoxidation.
- Regio: Markovnikov for HX/hydration/halohydrin (OH on more substituted carbon).
- Stereo: halogenation/halohydrin = anti; hydrogenation/dihydroxylation/epoxidation = syn; HX/hydration = not stereospecific.
- Rearrangements can occur in carbocation pathways (HX, acid hydration); three-membered intermediates/ concerted paths avoid them.