Physical Properties of Alkynes
Physical Properties of Alkynes
Alkynes behave much like other hydrocarbons of similar size, but the C≡C triple bond brings a few clear trends: slightly higher boiling points than the matching alkane/alkene, linear geometry, and a noticeably more acidic terminal ≡C–H (pKₐ ~25–26).
Boiling/melting trends
- Relative order (same carbon count): alkane ≲ alkene < alkyne (slightly higher for the alkyne).
- Example (C₂ series, approx. normal b.p.): ethane −88.6 °C; ethene −103.7 °C; ethyne −84.0 °C.
- Physical state vs chain length: C₂–C₄ gases (e.g., acetylene, propyne); ~C₅–C₁₅ liquids (e.g., 1-octyne, 1-decyne); longer chains become waxy solids as boiling/melting points rise.
Solubility and density
- Polarity: C≡C and C–H bonds are only weakly polar; overall, small alkynes are essentially nonpolar.
- Water: Insoluble or only very sparingly soluble (acetylene dissolves slightly; higher alkynes are effectively water-insoluble).
- Organic solvents: Readily soluble in nonpolar or weakly polar solvents (hexane, petroleum ether, benzene, ether, chloroform, acetone).
- Density: Liquid alkynes are less dense than water (~0.7–0.8 g/mL), so they float.
Acidity of terminal alkynes
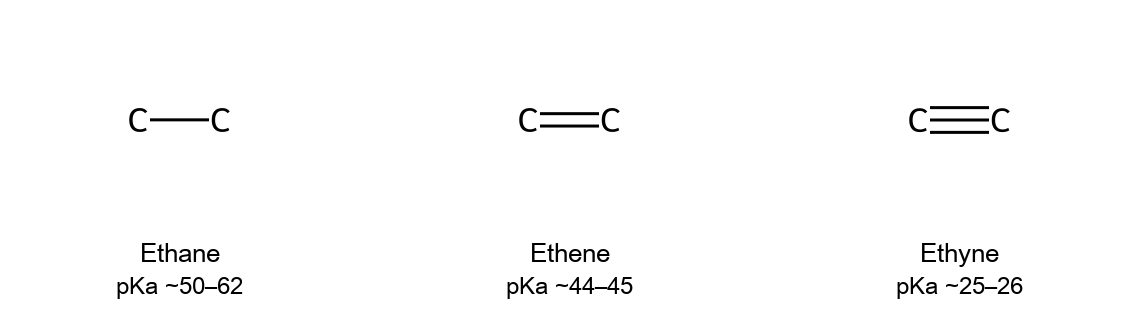
- Relative pKₐ (C₂ series): ethane ~50–62; ethene ~44–45; ethyne ~25–26. A terminal alkyne is therefore orders of magnitude more acidic than the matching alkane/alkene.
- Reason: The acetylide anion holds its lone pair in an sp orbital (50% s-character), which stabilizes negative charge more than the sp² (33%) or sp³ (25%) analogues.
- Consequences: Terminal alkynes (RC≡CH) can be deprotonated by strong bases (NaNH₂, NaH, organolithiums) to give acetylide salts—key nucleophiles for SN2 C–C bond formation on primary electrophiles. Internal alkynes lack a terminal ≡C–H and are not appreciably acidic under these conditions.
Summary
- Boiling points: alkynes are slightly higher than the corresponding alkane/alkene; small are gases, mid-size liquids, long chains solids.
- Solubility/density: nonpolar; insoluble in water; soluble in nonpolar organics; liquid alkynes float on water.
- Acidity: terminal ≡C–H (pKₐ ~25–26) is far more acidic than alkane/alkene C–H, enabling acetylide formation with strong base for C–C bond construction.