Synthesis and Reactions of Alcohols and Ethers
Alcohols and ethers are important functional groups in organic chemistry that can be synthesized through various methods and undergo a wide range of reactions. In this lesson, we will discuss the synthesis and reactions of alcohols and ethers.
Synthesis of Alcohols
Alcohols can be synthesized through a variety of methods including:
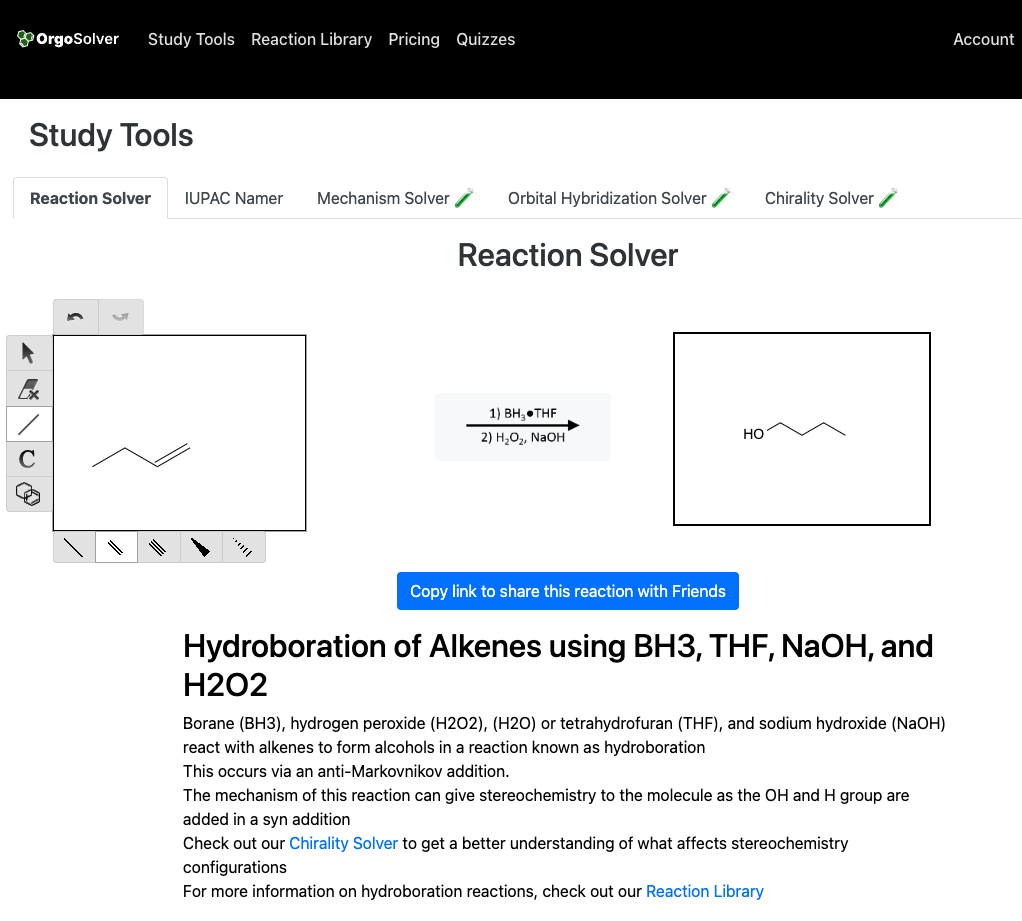
Hydroboration-oxidation of alkenes: In this method, the alkene is treated with borane (BH3) followed by oxidation with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to yield an alcohol.
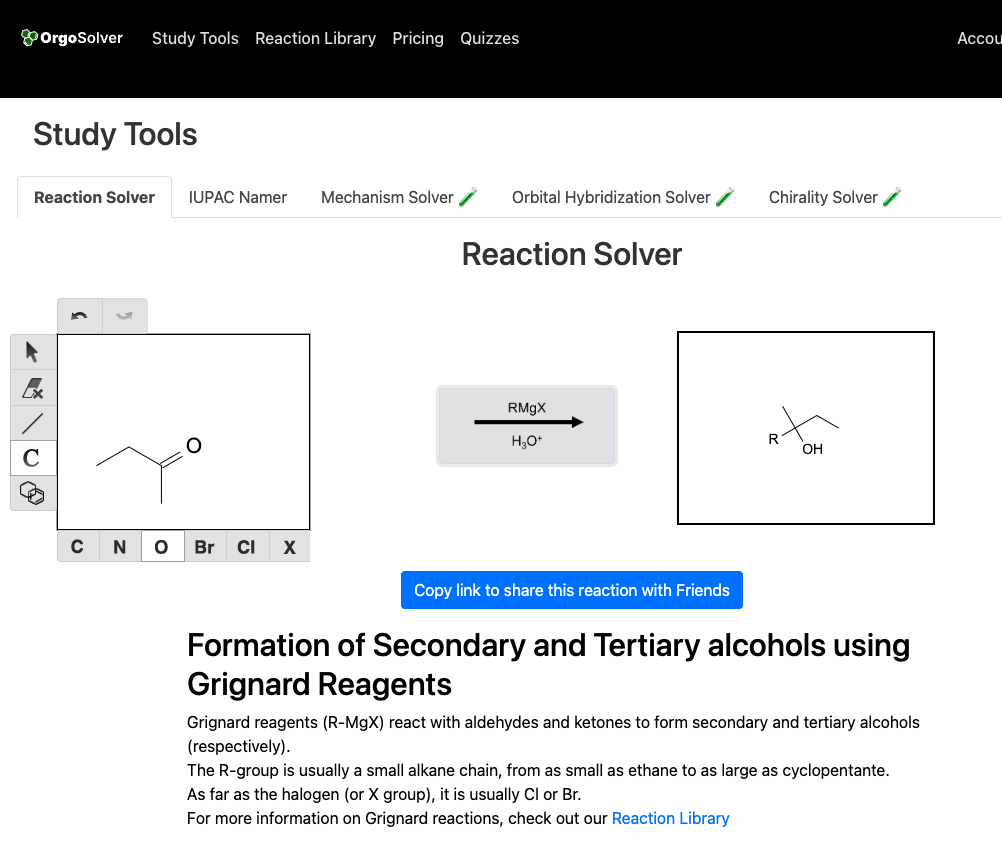
Grignard reaction: In this method, an alkyl or aryl magnesium halide (Grignard reagent) is reacted with a carbonyl compound (aldehyde or ketone) in the presence of a proton source (water, alcohol or acid) to produce an alcohol.
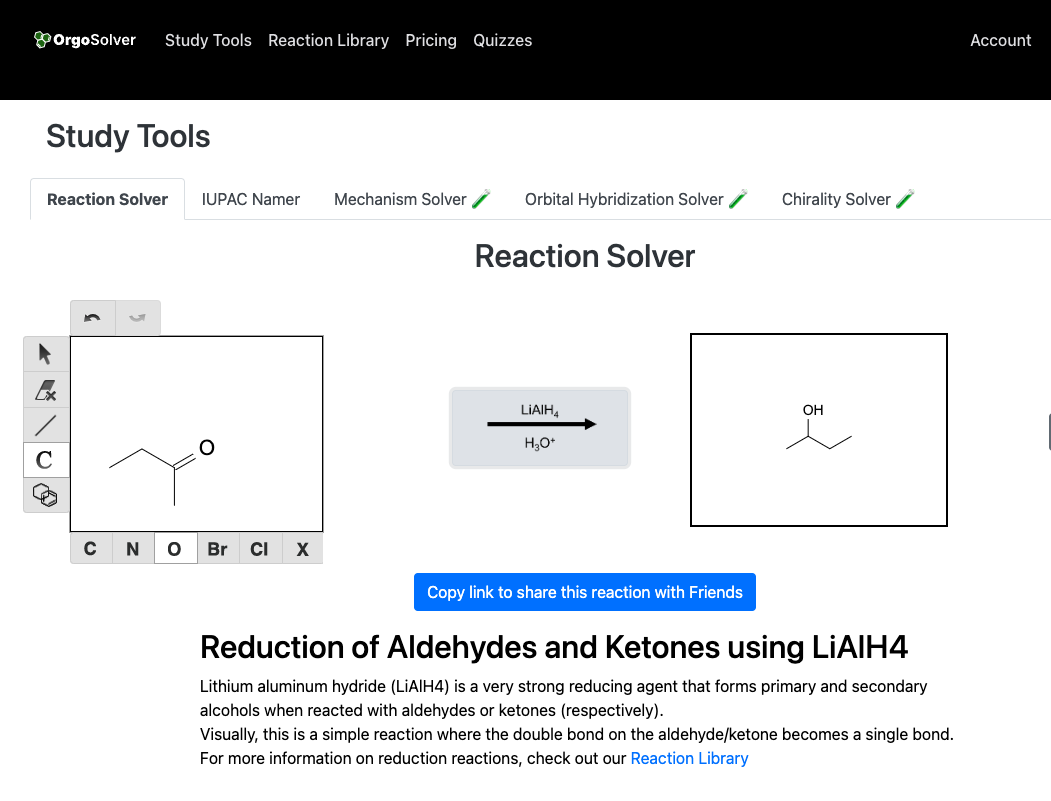
Reduction of carbonyl compounds: Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced to alcohols using reducing agents such as sodium borohydride (NaBH4) or lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4).
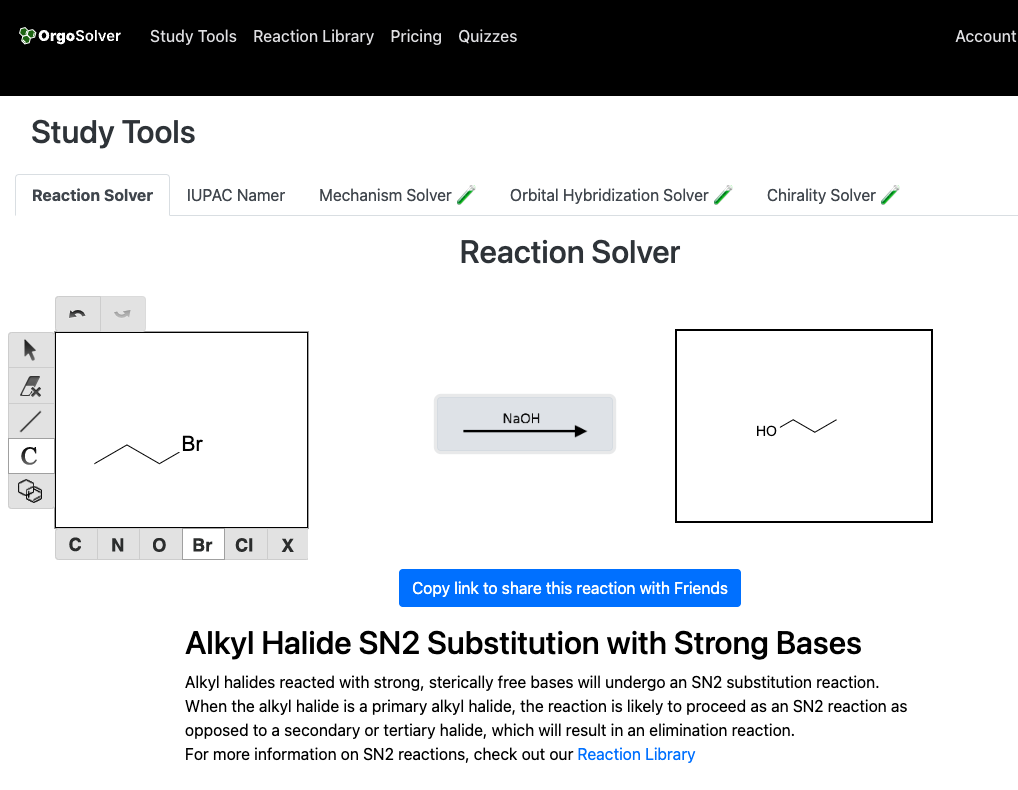
Substitution of alkyl halides: Primary and secondary alkyl halides can be converted to alcohols using a strong base such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
Synthesis of Ethers:
Ethers are most commonly synthesized through the Williamson ether synthesis: In this method, an alkoxide ion (generated by treating an alcohol with a strong base) is reacted with an alkyl halide or an aryl halide to yield an ether.
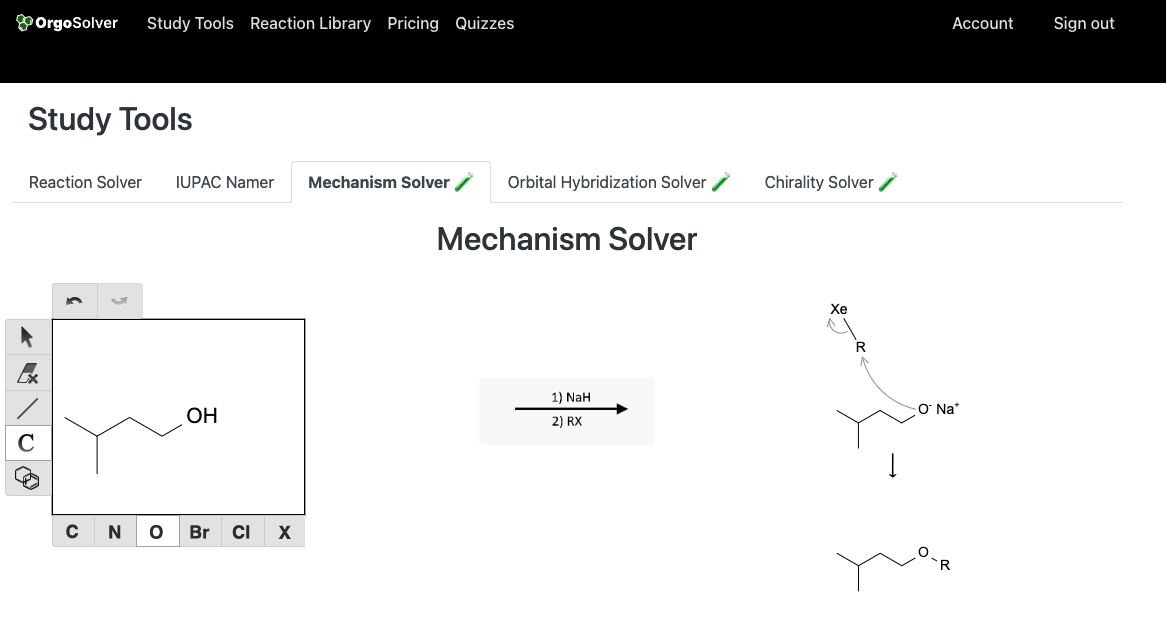
Reactions of Alcohols:
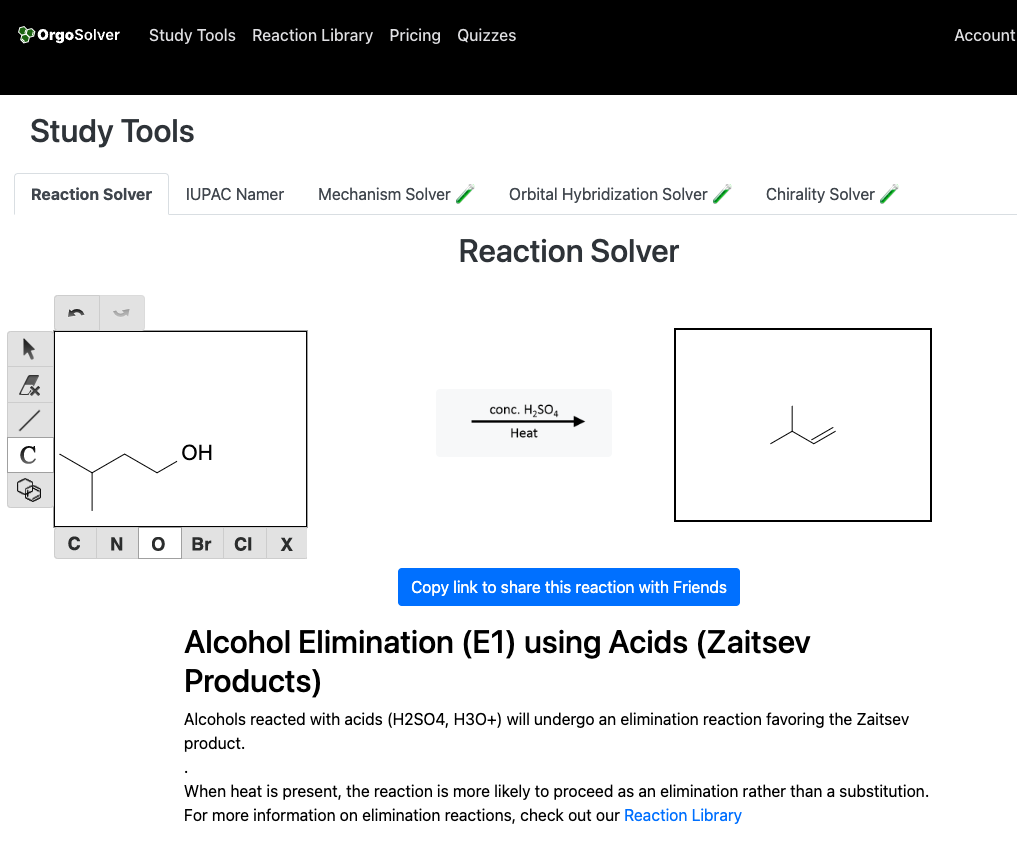
Dehydration: Alcohols can be dehydrated to form alkenes through the elimination of water. This reaction is typically catalyzed by an acid catalyst, such as sulfuric acid.
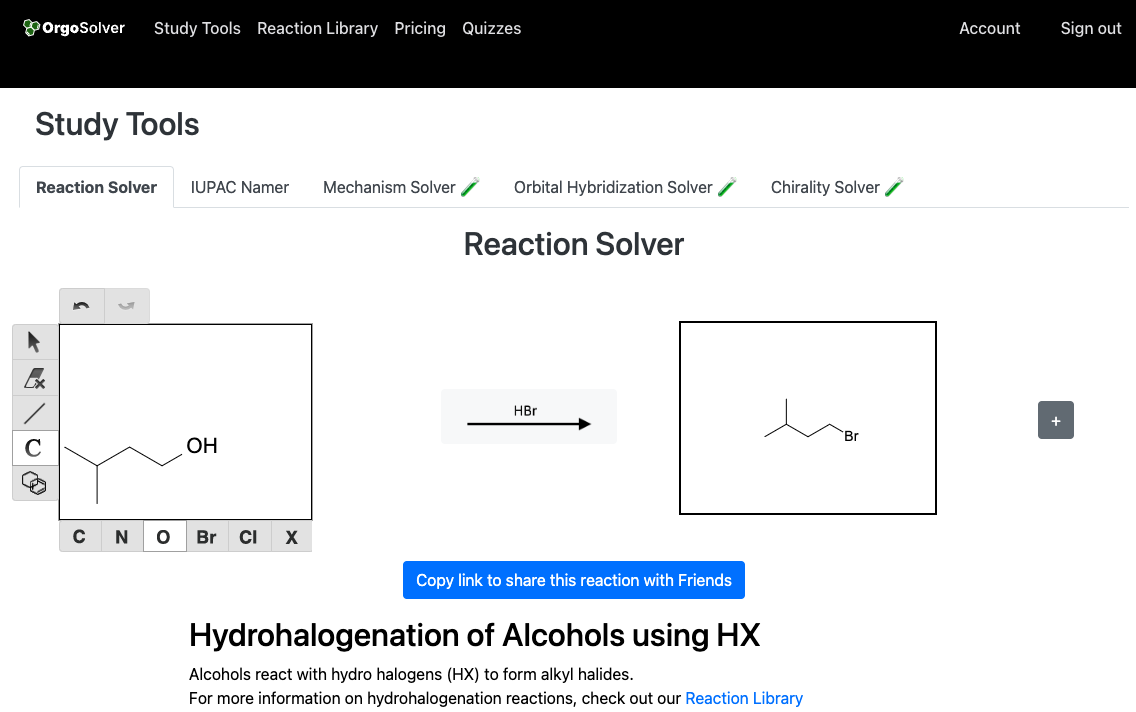
Substitution: Alcohols can undergo substitution reactions with hydrogen halides, in the presence of a strong acid catalyst, to yield alkyl halides.
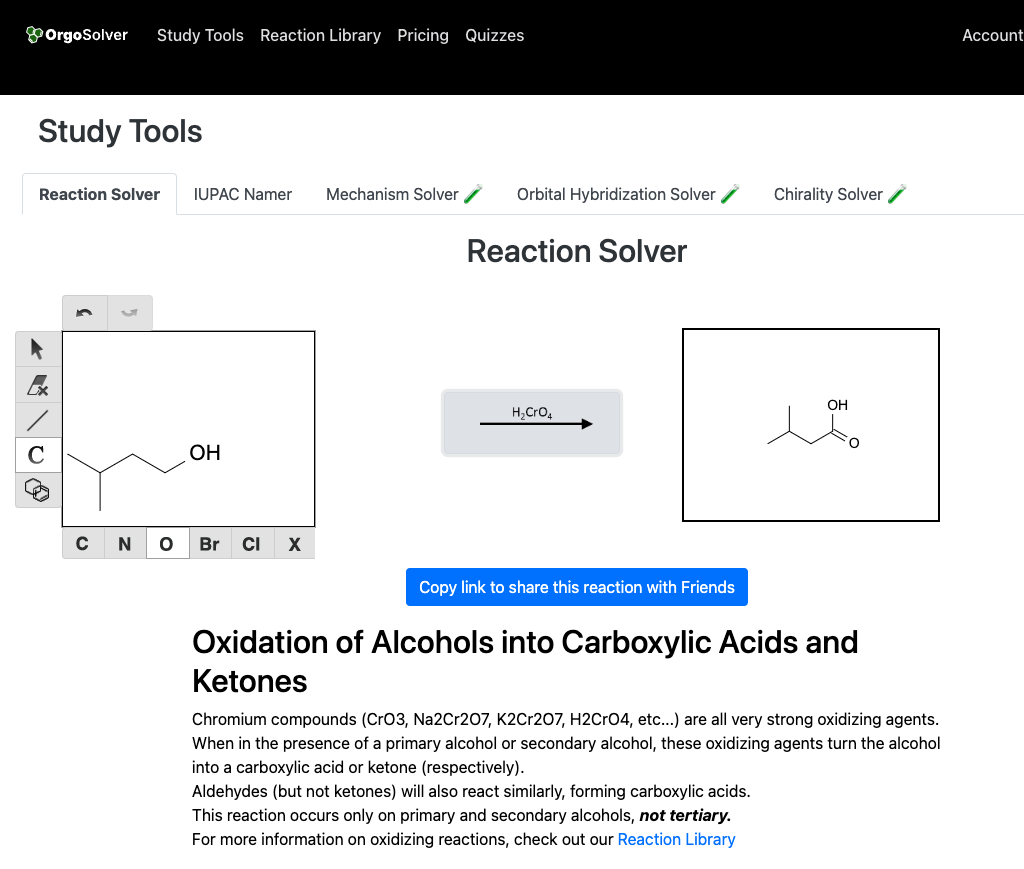
Oxidation: Primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or carboxylic acids, while secondary alcohols can be oxidized to ketones. This reaction is typically catalyzed by an oxidizing agent, such as potassium permanganate or chromium (VI) oxide.
Reactions of Ethers:
Cleavage: Ethers can undergo cleavage reactions to form alcohols and alkyl halides in the presence of a strong acid catalyst, such as hydrobromic acid (HBr).
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis: Ethers can be hydrolyzed to yield two alcohols through the addition of water in the presence of an acid catalyst, such as sulfuric acid.
Summary
Alcohols and ethers are important functional groups in organic chemistry that can be synthesized through various methods and undergo a wide range of reactions. Alcohols can be synthesized through hydroboration-oxidation of alkenes, Grignard reactions, reduction of carbonyl compounds, and oxidation of alkyl halides. Ethers can be synthesized through Williamson ether synthesis.
Visit our Reaction Solver to draw any molecule, select your reagent, and get an answer!
Test Your Knowledge:
What functional groups can be used to synthesize alcohols?
How are ethers synthesized?