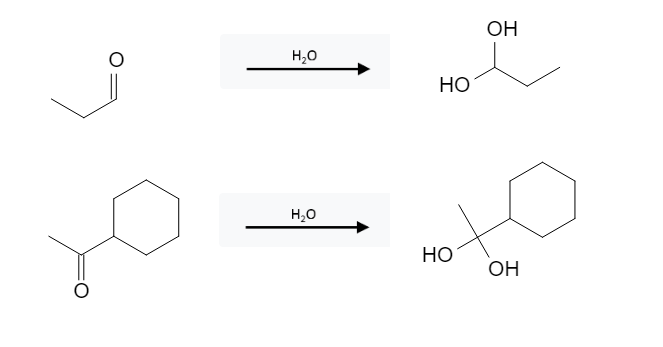
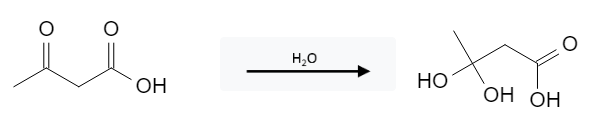
Aldehyde Reactions: Geminal Diol Formation from Aldehyde, Ketone using H2O
Geminal diols can be formed from aldehydes and ketones using water in a hydration reaction:
The reaction requires an aldehyde/ketone; it will not react with carboxylic acids:
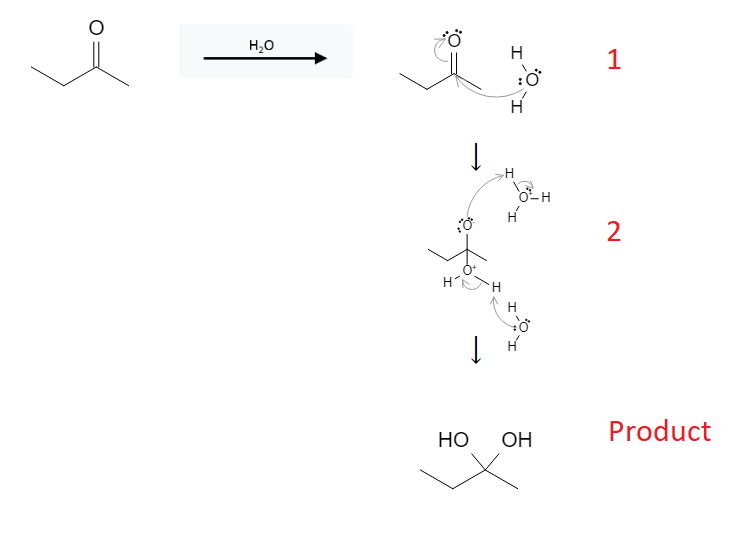
The reaction mechanism is depicted below:
In the first step, the lone pair of electrons from the water molecule attack the ketone carbon atom, forming a bond between the water molecule and the ketone molecule. This also breaks the carbon-oxygen bond sending the electrons to the oxygen atom.
In the second step, the conjugate acid H3O+ is attacked by the negatively charged ketone-oxygen atom. Simultaneously, a water molecule attacks the newly attached H2O group, removing a proton and sending the lone pair of electrons to the oxygen atom..