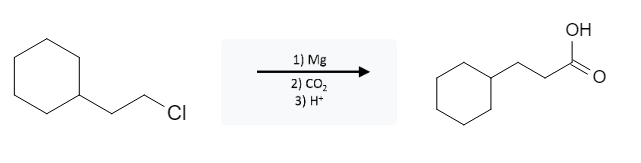
Alkyl Halide Reactions: Carboxylic Acid formation using Alkyl Halides, Mg, and CO2
Alkyl halides (R-X) that are reacted to form Grignard reagents (RMgX) can react with carbon dioxide (CO2) in acidic environments to form carboxylic acids:
This reaction is pretty straight forward; the halogen group is replaced with the carbon atom of the carboxylic acid group. This reaction may be presented in a different way where the alkyl halide has already formed a Grignard reagent by adding Mg. The halogen group can be Cl, Br, or I.
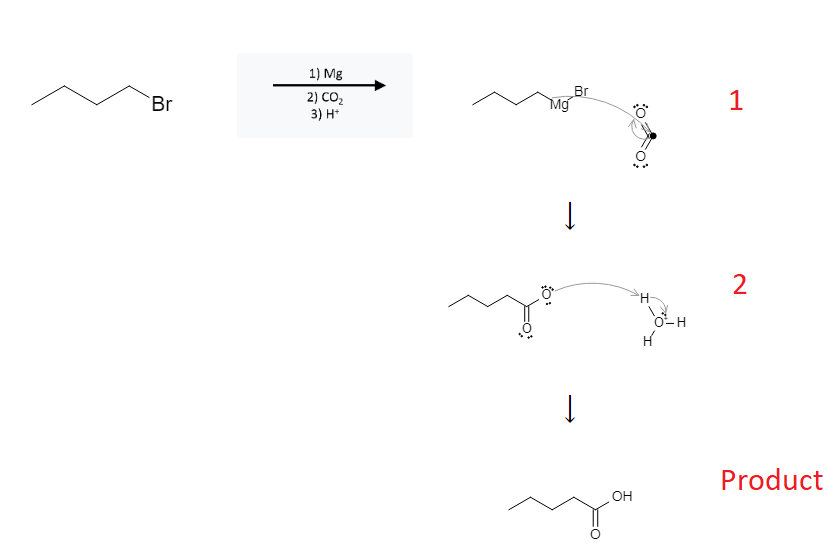
The reaction mechanism is depicted below:
In the first step, the magnesium is added to the molecule and takes its place between the carbon atom and the halogen atom. Then, the electrons from the carbon-magnesium bond attack the carbon dioxide-carbon atom, breaking the carbon-magnesium bond.
In the second step, the electronegative oxygen attacks a nearby H3O+ proton, completing the reaction.