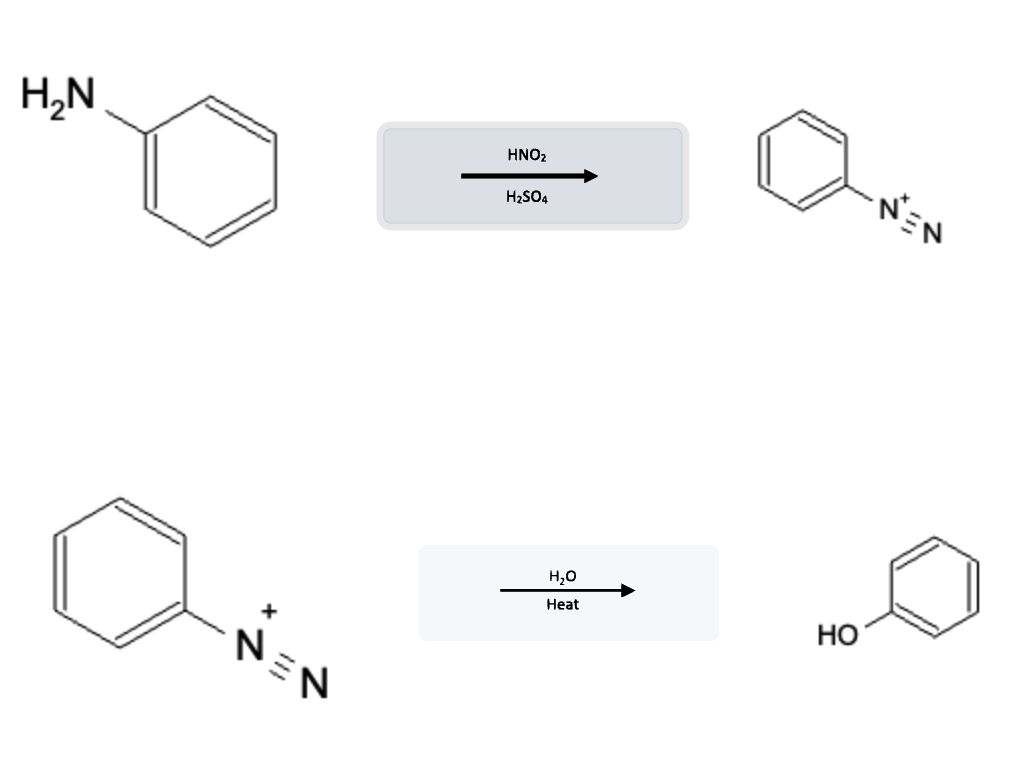
Aromatic Reactions: Phenol formation from Diazonium Salts using H2O and Heat
Diazonium salts react with water (H2O) under hot temperature conditions to form phenol. This reaction is commonly performed in organic chemistry labs to convert aromatic amines (aniline) into phenols, using HNO2/H2SO4 reaction as an intermediate step for synthesis:
Combination of Aniline to Diazonium Salt to Phenol
Mechanism
The reaction mechanism is depicted below:
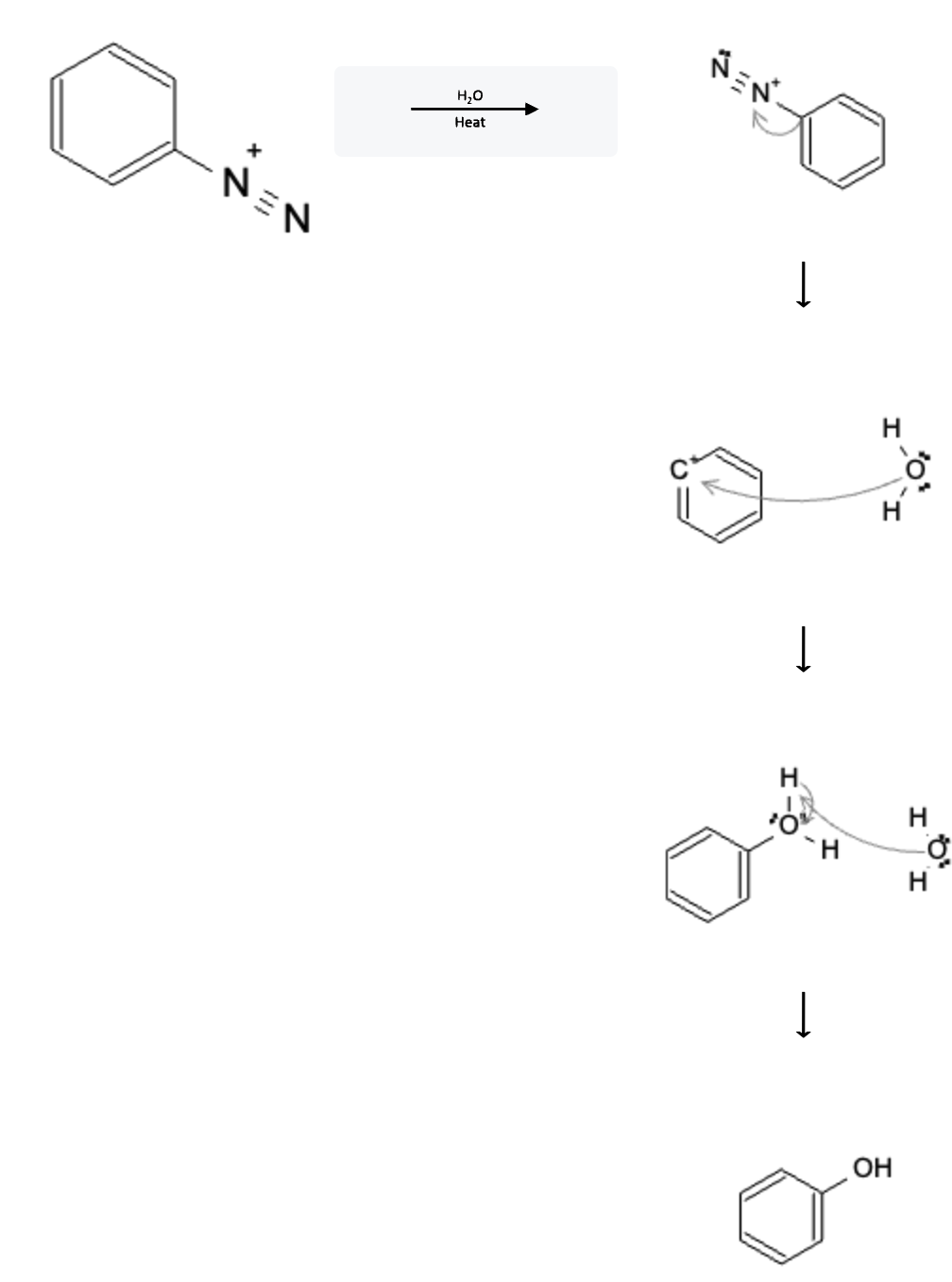
In the first step, the heat from the reaction forces the N≡N moiety off the molecule, forming nitrogen gas (N2) and leaving behind a positive charge on the benzene ring.
In the second step, a water molecule attacks the positively charged carbon on the benzene ring, attaching itself to that location.
In the third step, another water molecule deprotonates the connected water molecule, resulting in the final phenol product.
Practice this reaction using our Reaction Solver!