Alkyne Structure and Nomenclature
Alkyne Structure and Nomenclature
Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one carbon–carbon triple bond. They follow the general formula CₙH₂ₙ₋₂, are linear at the triple bond (sp hybridized, 180°), and are more reactive and notably more acidic at a terminal ≡C–H (pKₐ ~25–26) than the analogous alkenes or alkanes.
- How to name alkynes
- Geometry and formula
- At-a-glance properties
- Worked examples (naming + visualization)
- Summary
How to name alkynes
- Choose the longest chain containing the triple bond, number from the end that gives the triple bond the lowest locant, and use the suffix “–yne.”
- Indicate the triple-bond position with a number (e.g., pent-2-yne has the triple bond starting at carbon 2).
- Multiple triple bonds use “diyne,” “triyne,” etc., with locants for each.
Example:
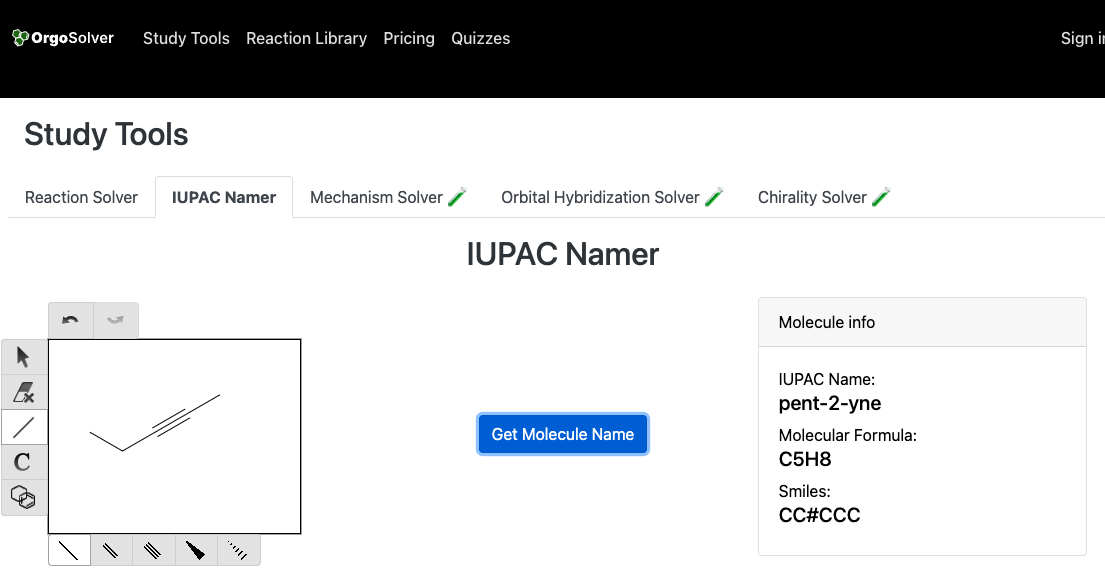
Try our Organic Compound Namer to confirm structures and IUPAC names.
Geometry and formula
- Hybridization: sp on the triple-bond carbons → linear (180°) with one σ bond and two π bonds.
- Formula: CₙH₂ₙ₋₂ (same as a diene), reflecting two degrees of unsaturation.
- Electronegativity/acidic H: The 50% s-character of sp carbon stabilizes the conjugate base of terminal alkynes, making ≡C–H notably more acidic (pKₐ ~25–26) than alkene/alkane C–H.
- Terminal vs internal: Terminal alkynes (1-ynes) have a triple bond at C1 and an acidic ≡C–H that can form an acetylide with strong base; internal alkynes (2-ynes, 3-ynes, etc.) have no terminal ≡C–H.
At-a-glance properties
- Similar boiling/melting trends to alkenes/alkanes of the same size, but more reactive due to two π bonds.
- Linear geometry; nonpolar overall (terminal ≡C–H is only weakly polar).
- Undergo addition reactions (see the reactions overview) and can be deprotonated at a terminal ≡C–H to form acetylides.
- No cis/trans (E/Z) isomerism about a single C≡C: the substituents are colinear with the linear triple bond.
- Terminal ≡C–H acidity matters synthetically: deprotonate with very strong bases (NaNH₂, organolithiums); weaker bases like hydroxide/alkoxides are not sufficient.
- Physical properties (boiling point/solubility) are broadly similar to alkenes of the same carbon count; size and dispersion dominate trends.
Worked examples (naming + visualization)
Below are five sample alkynes (≥5 carbons). Atom numbers in each image are shown along the longest chain to make the locants for the triple bond clear. These mirror common alkyne nomenclature practice problems.
| Molecule name | Structure (numbered) | Short explanation |
|---|---|---|
| pent-2-yne |  | Five carbons; triple between C2–C3 (internal alkyne, lowest locant). |
| hex-3-yne | 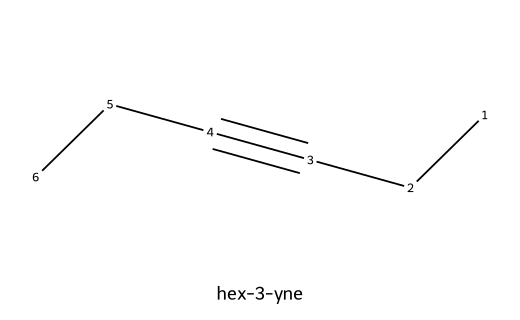 | Six carbons; symmetric internal triple bond at C3. |
| hept-2-yne | 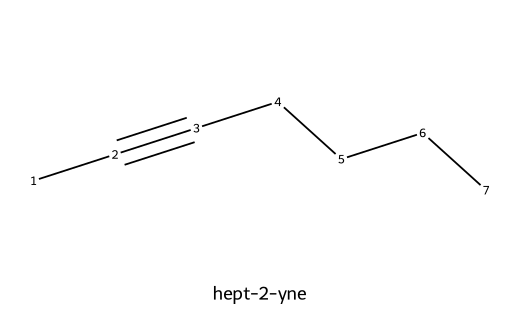 | Seven carbons; triple between C2–C3 (internal alkyne; no terminal ≡C–H). |
| 4-methylpent-2-yne | 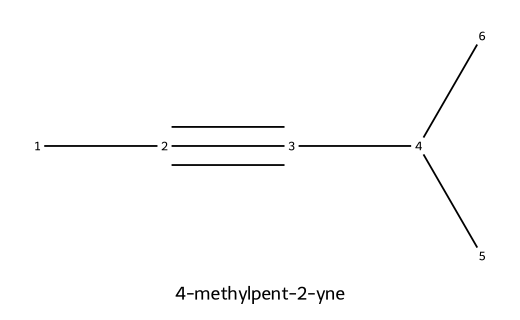 | Pent parent; triple at C2; methyl substituent at C4 (numbers on the main chain). |
| 5-bromopent-2-yne | 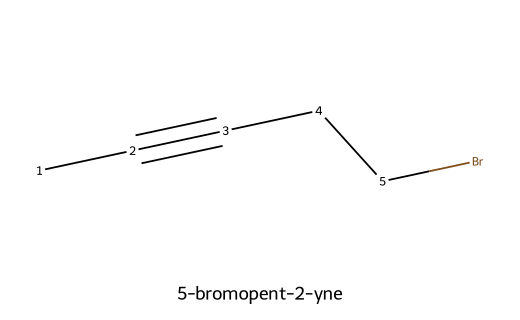 | Pent parent; triple at C2; bromo substituent at the terminal C5. |
Summary
- Naming: Longest chain with the triple bond; lowest-numbered triple bond; suffix “–yne.”
- Geometry: sp, linear, 180°; formula CₙH₂ₙ₋₂.
- Reactivity: Two π bonds enable additions; terminal ≡C–H is significantly more acidic than alkene/alkane C–H (→ acetylide formation with strong base); no cis/trans assignment around a single C≡C.