Acid-base properties of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) as the functional group. They are weak acids due to the acidic proton on the carboxyl group. In this article, we will explore the acid-base properties of carboxylic acids.
Carboxylic acids are weak acids that can donate a proton to a base. When carboxylic acids are dissolved in water, they undergo dissociation to form carboxylate ions (RCO2-) and hydronium ions (H3O+). The dissociation is a reversible reaction, and the equilibrium constant is called the acid dissociation constant (Ka).
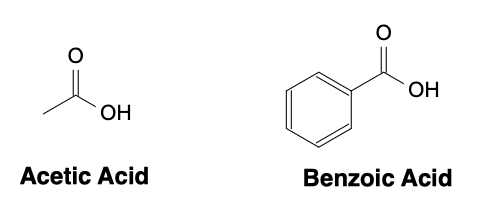
The Ka value of a carboxylic acid depends on the strength of the acid. The stronger the acid, the larger the Ka value. The Ka value can be used to predict the acidity of a carboxylic acid. A lower pKa value indicates a stronger acid. For example, acetic acid (CH3COOH) has a pKa of 4.76, while benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) has a pKa of 4.20. Therefore, benzoic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
Carboxylic acids can also react with bases to form carboxylate salts. The reaction is called acid-base neutralization. The carboxylic acid donates a proton to the base to form a carboxylate ion and a neutral molecule. The carboxylate ion is a conjugate base of the carboxylic acid.
In addition to acid-base reactions, carboxylic acids can also undergo esterification, amidation, and decarboxylation reactions. Esterification involves the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to form an ester. Amidation involves the reaction of a carboxylic acid with ammonia or an amine to form an amide. Decarboxylation involves the loss of a carbon dioxide molecule from a carboxylic acid to form an alkane.
For a complete list of carboxyl reactions used in Organic Chemistry 1, check out our Reaction Library!
Visit our Reaction Solver to draw any molecule, select your reagent, and get an answer!
Summary
Carboxylic acids are weak acids that can donate a proton to a base. The acidity of a carboxylic acid can be predicted using its Ka or pKa value. Carboxylic acids can react with bases to form carboxylate salts and can undergo esterification, amidation, and decarboxylation reactions.
Test Your Knowledge:
What is the acid dissociation constant (Ka) for a carboxylic acid, and how does it relate to the strength of the acid?
What is esterification, and how does it differ from amidation and decarboxylation reactions?